VIDEO: How Our PRC-155 Manpack Radio Connects U.S. Armed Forces To The MUOS Satellite Network.
MUOS A Next Generation Satellite Communications Network
The Mobile User Objective System (MUOS) is the U.S. Navy's next-generation satellite communications system that provides simultaneous voice, video and data communications for U.S. Armed Forces anytime and anywhere in the world. General Dynamics Mission Systems is currently under contract with Lockheed Martin to provide the user-entry and integrated ground segments for the MUOS program. MUOS will replace the military's current narrowband tactical communications system, known as the Ultra High Frequency Follow-on (UFO) system.
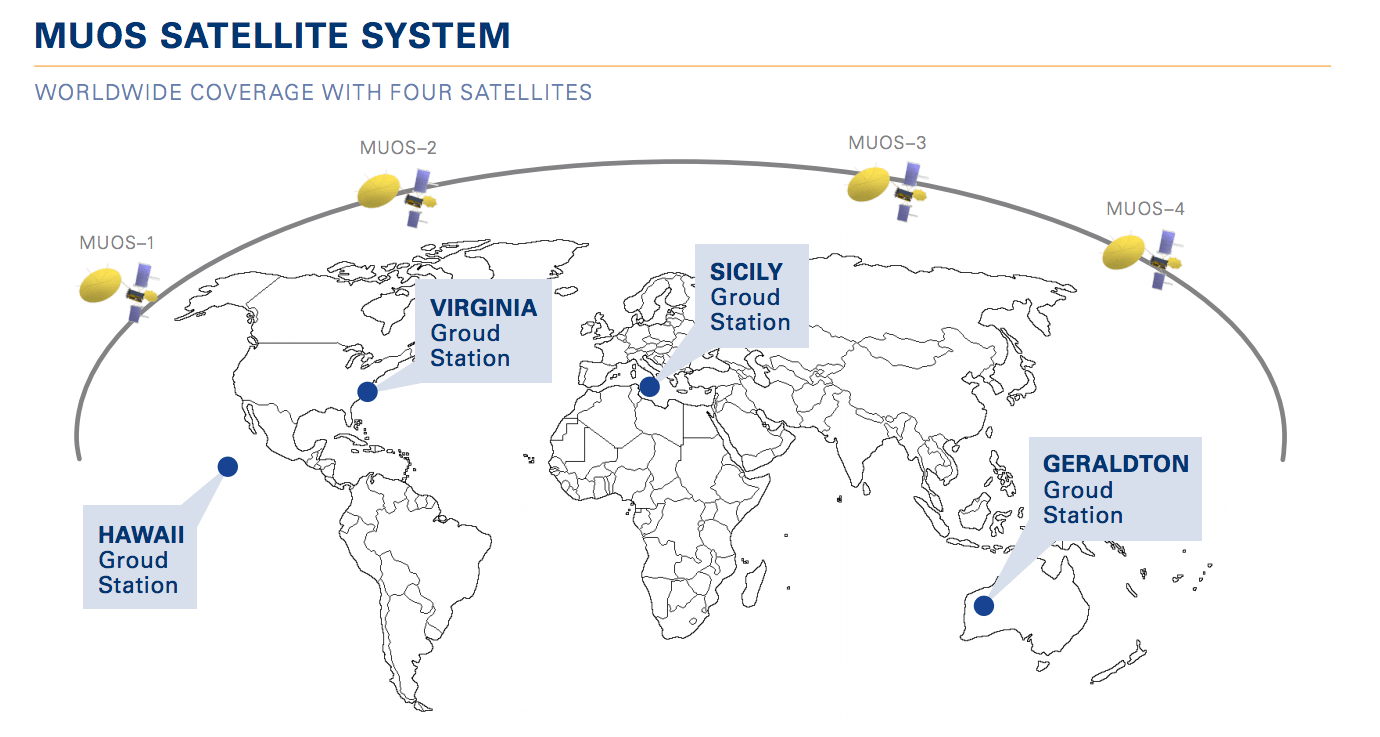
MUOS Ground Stations
General Dynamics leads the deployment of the MUOS ground system, which includes four ground station facilities positioned around the globe to assist in the management and operation of the orbiting satellites. Each ground station is equipped with three freestanding Ka-Band antennas, which act like cell phone switches, receiving radio calls relayed through the MUOS satellites. The system provides a familiar cellular phone-like service, allowing forces on the ground to communicate directly with each other and their commanders regardless of location, at higher levels of quality and much greater capacity than available today.
Ten Times More Capacity Than Legacy System
MUOS offers cell phone quality voice communications to soldiers at ten times the capacity of the legacy UHF system. A single MUOS satellite provides 4x the capacity of the entire legacy system of eight satellites. For U.S. Forces on the ground, the MUOS system will provide familiar cellular phone-like services with the satellites acting as very tall towers to allow warfighters on the ground to communicate directly with each other and their commanders virtually anywhere in the world.
Waveform Development / WCDMA
MUOS radio calls, like those recently demonstrated in the Arctic Circle with the PRC-155 Manpack radio, use the MUOS waveform. Developed by General Dynamics engineers in Scottsdale, AZ, the waveform converts a commercial third generation (3G) Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) cellular phone technology to provide a new and more capable UHF military satellite communications (SATCOM) system.



